

| Technical Guide > Server Manager Introduction > DMZ Services |
DMZ Services enables Service Root and Application configurations to be made.
The Service Root is the base URL used by various application services in Temenos Infinity.
 |
Typically the name of the server is entered (http://[YOUR SEVER NAME HERE]/). If using a load balanced environment, the name of the load balancer is entered. |
All installed applications use the root URL to append a specific virtual directory for an application to derive the complete URL.
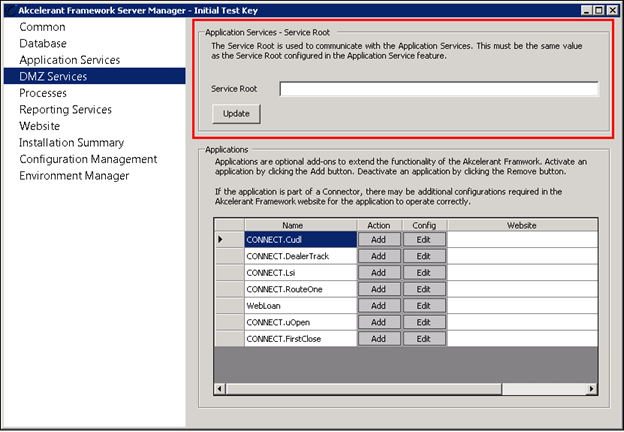
DMZ application services enable connectors, such as Virtual Capture, CUDL, Dealertrack and RouteOne to be implemented post installation of Temenos Infinity.
DMZ application services differ from standard application services in that they must be hosted on a public-facing server. Connectors such as CUDL, Dealertrack and RouteOne require inbound communication to the server in order to transmit applications to Temenos Infinity. Without public access via the DMZ services, these providers cannot communicate with Temenos Infinity. Communications with the DMZ are relayed to complimentary internal services behind the internal firewall.
 |
These complimentary services must be installed. For more information on complimentary services, refer to the Application Services section within this guide. |
To add a DMZ application, click the Add button.
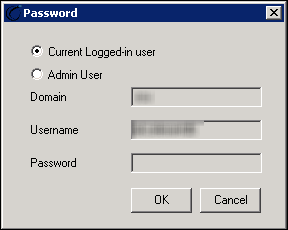
A prompt appears to install the service using the Currently Logged-in user or an Admin User.
Once the user is chosen, select the Website, Virtual Directory and URL Root.
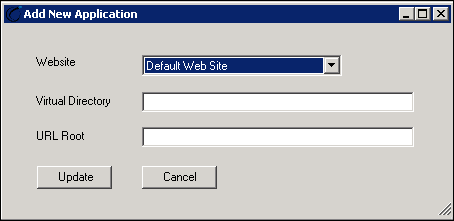
Select the DMZ service’s website. By default, the Website populates with Default Web Site, however additional choices are available in the provided drop-down list. The Virtual Directory indicates the application service being installed, such as CUDL DMZ or Dealertrack DMZ. The URL Root is a fully qualified domain name. For example, https://[Akcelerant.ABCCreditUnion.org]/. Once the Website, Virtual Directory and URL Root are identified, click Update to install the DMZ application service.
Refer to the diagram below to better understand the relationship between DMZ services and internal Application services.

Third parties (1) requiring inbound communication (First Close and Route One) and customers of the financial institution (2) accessing public facing services (Web Loan) transmit through the DMZ firewall (3). Once beyond the firewall, they are able to connect to the Public Web Server (4). This server relays communication through the internal LAN firewall (5) and the load balancer until received on the internal Application Server (6) for processing. This configuration ensures institutions can safely allow incoming connections without allowing direct access to internal servers.